You may not know the name Joe Rosenthal, but you have seen his work. Rosenthal was a photographer for the Associated Press (AP). On the afternoon of February 23, 1945, in 1/400th of a second, Joe Rosenthal took one of the most iconic photographs in American history. Seven decades later, his image of six United States Marines in combat gear raising an American flag still captivates the mind and stirs the soul.
The photograph inspired a famous sculpture that is now recognized around the world as a symbol of the United States Marines. Known officially as the United States Marine Corps War Memorial, it is dedicated “For the Marine dead of all wars, and their comrades of other services who fell fighting beside them, since the Marine Corps’ founding in 1775”.
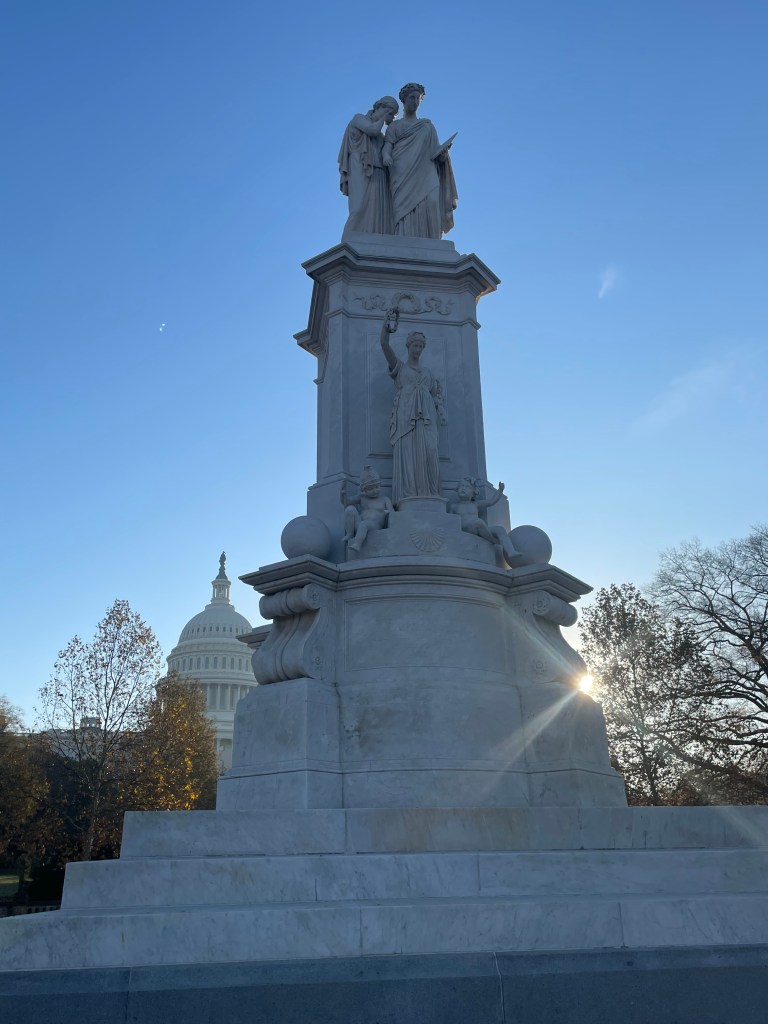
The memorial is located in Arlington Ridge Park, a broad, open green space on the edge of the busy Arlington neighborhood of Rosslyn and in close proximity to Arlington National Cemetery. Situated on high ground overlooking the Potomac River, the park is a natural venue for the memorial.

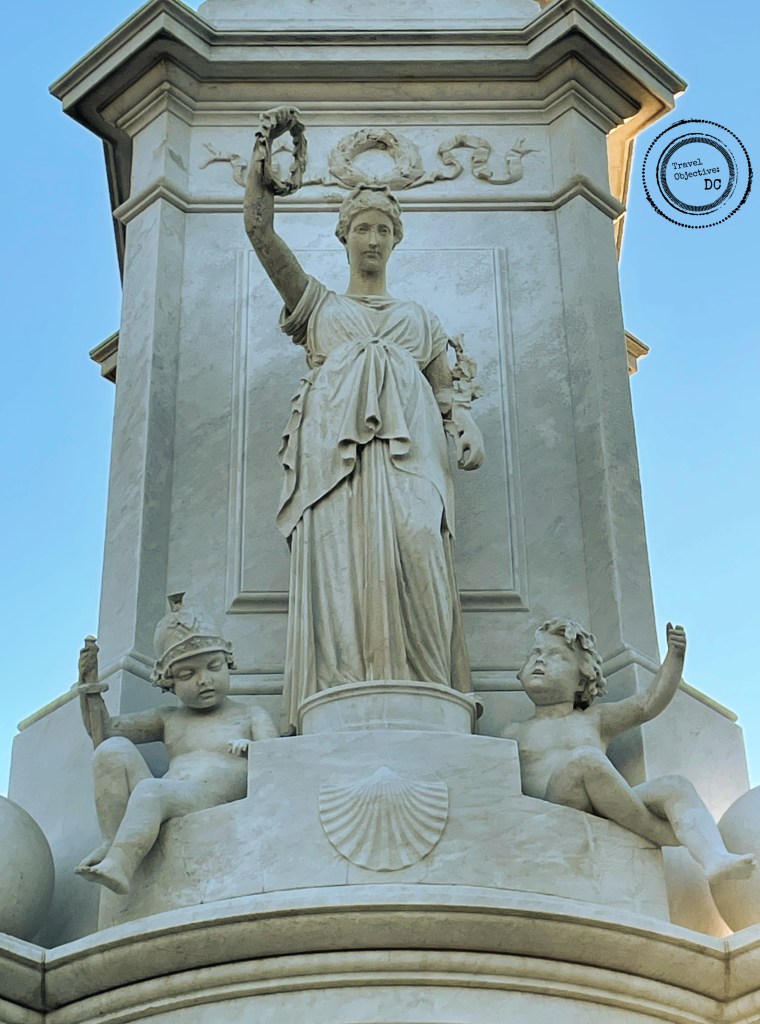
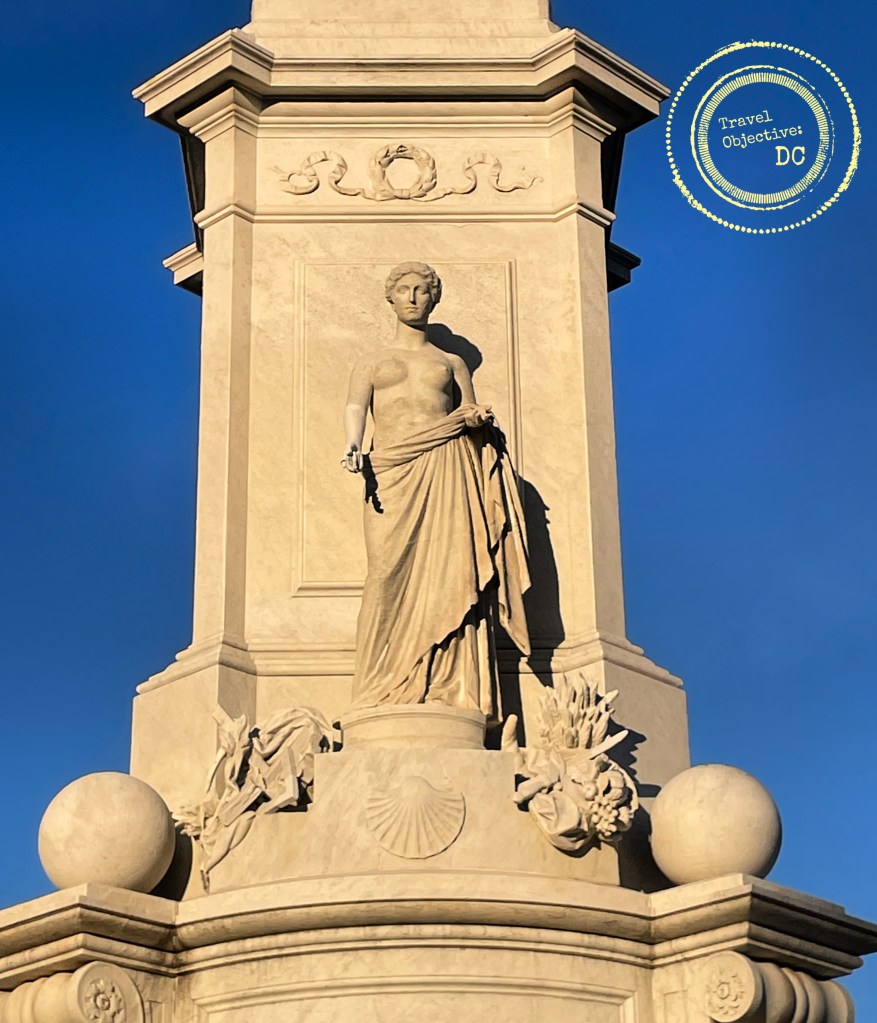
Upon approaching the memorial, the first impression is of its size. The entire monument is more than five stories high. The thirty-two foot bronze figures of the Marines stand on a polished, black granite oval base. A green patina on the bronze adds color to the figures’ carefully sculpted fatigue uniforms.
Around the base of the statue, notable battles fought by United States Marines from the Revolutionary War through the present day are engraved in gold lettering. Fleet Admiral Chester Nimitz’s observation that among those Americans who served on Iwo Jima, “uncommon valor was a common virtue” is prominently inscribed on the west side of the memorial.
A circular trail around the park features interpretive signs providing background information on the Battle of Iwo Jima, the famous photograph, facts about the statue, and the history and missions of the US Marines.

A miniature statue for the vision impaired included on an interpretive sign near the memorial.
The Marine Corps traces its history back to 1775 when the Continental Congress authorized the recruitment of two battalions of Marines to provide the fledging Continental Navy with a ground operations force. Since then, the Marines have engaged in every major conflict and a number of expeditionary operations. As the Marine Corps Hymn declares, the Marines have “fought in every time and place…” including some places you might not expect, such as the Civil War’s First Battle of Bull Run and the Battle of Belleau Wood during World War I.
In the decades before World War II, the Marine Corps developed and refined the doctrines, tactics and training for amphibious landing operations, where Marines would storm ashore from landing craft prepared to fight. Their proficiency in these complicated maneuvers was instrumental to the success of the Allied “island hopping campaign” in World War II’s Pacific theater. In early 1945, the island of Iwo Jima became the next strategic objective. By this time in the war, US B-29 Superfortress bombers could reach the main Japanese islands from airstrips on Guam and Saipan. However, both the airstrips and the B-29 in-flight formations were often attacked by Japanese fighters based on Iwo Jima.
As they prepared, the Marines knew Iwo Jima would be a tough fight. Unlike earlier battles, the Marines would be landing on Japanese territory, not an occupied island. The Imperial Japanese Army had approximately 23,000 soldiers on Iwo Jima, occupying an extensive tunnel and fortification system.
On February 19, 1945, approximately 70,000 Marines and Navy support personnel landed on Iwo Jima. After days of heavy fighting, Marines of the 2nd Battalion, 28th Marine Regiment made steady progress in their mission to capture Mount Suribachi, a dormant volcano that was the highest point on the island. By the morning of February 23, they reached the summit.

The first Iwo Jima flag raising. A small flag carried ashore by the 2nd Battalion, 28th Marines is planted atop Mount Suribachi on February 23, 1945.
– Staff Sergeant Louis R. Lowery, USMC
At the top, an American flag was raised so that troops across the island would see the Marines now held the high ground. At the sight of the flag, Marines cheered and Navy ships sounded their horns.
But the flag was only about 4-feet-long and not quite visible at a distance. A few hours later, an 8-foot-long flag was acquired and sent up to the Marines on Mount Suribachi. As six Marines quickly planted the second flag, Joe Rosenthal captured the moment for posterity.
Once the flag was raised, the Marines quickly dispersed as fierce fighting continued. Four more weeks of intense combat were yet to come. The landing force sustained 24,053 causalities, roughly one third of those who landed. Three of the men in the photo were among the 6,140 Marines and Navy corpsmen who would lose their lives on Iwo Jima, the deadliest battle ever for the Marine Corps.
But there were instances of great heroism as well. Twenty-seven men were awarded the Medal of Honor for their service at Iwo Jima (about half of them were presented posthumously).
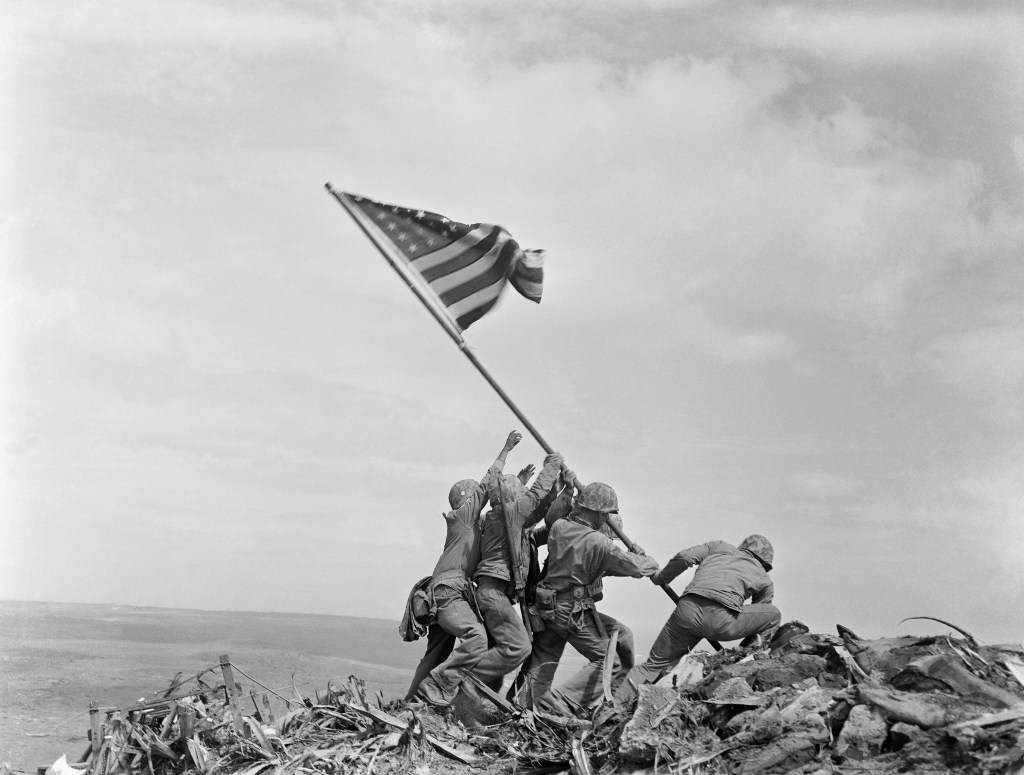

Joe Rosenthal was carefully balancing himself on some rocks and sandbags as he quickly snapped his famous photograph without using the viewfinder.
He was unaware of how the picture would turn out as he sent the film to Guam for developing a few hours after taking the photo. The developed pictures crossed the desk of an AP photo editor named John Bodkin. Bodkin’s job was to scan through the photos submitted by his photographers across the Pacific theater for use in American newspapers. Upon seeing Rosenthal’s picture, he knew it was special, proclaiming “Here’s one for all time!”
He immediately arranged to transmit the picture to the AP Headquarters in New York. It arrived in time to be printed on the morning of February 25th in the Sunday editions of newspapers all over the United States. The photograph was an instant sensation. The previous week’s grim news of the terrible combat and heavy casualties on Iwo Jima were now replaced by a picture showing American progress and determination. Rosenthal won the Pulitzer Price for the photo and it would become the main symbol of the 7th US War Loan campaign.

US Department of the Treasury poster for the 7th War Loan. The campaign would raise over $26 billion during the spring of 1945.
Sculptor Felix W. de Weldon, an artist on active duty with the US Navy, was one of the millions who saw the image. Captivated by the photograph, he began modeling the image in clay, then building a life size representation.
He proposed building a grand monument based on Rosenthal’s photograph. With the consent of both Congress and the Marine Corps he began working on plaster models from which bronze castings for the statue were made.
A private fundraising campaign was begun to build the statue based on de Weldon’s work. Over $850,000 was raised from Marines, veterans, and other supporters. He modeled the faces, frames and other features of three men who survived the battle and were believed at the time to be in the photo. He used photographs and information about the fallen Marines to model their images.

After years of hard work, the memorial was dedicated by President Dwight D. Eisenhower on November 10, 1954. In 1961, President John F. Kennedy signed a proclamation authorizing the US flag to be flown at the memorial 24 hours a day.
Shortly after the photo was taken, there were issues with identifying the men in the picture. Rosenthal did not record the names of his subjects and his picture shows no faces. An event that took about ten seconds became a distant memory in the face of the intense fighting on Iwo Jima. The initial efforts to identify the figures lead to unfortunate errors. The first misidentification was corrected in 1947 as Corporal Harlan Block was identified as the Marine planting the flag pole into the ground. For many decades it was believed a Navy Corpsmen named John Bradley and a Marine named Rene Gagnon were in the photograph.
In the 2010’s researchers studying Rosenthal’s and other photographs (there were both Army and Marine Corps photographers present at the time) of the flag raising carefully examined the uniforms and equipment of the flag raisers. They concluded that two different Marines and neither John Bradley nor Rene Gagnon were actually in the photograph. The Marines convened two official Boards of Inquiry, one in 2016 and another in 2019. After thorough examinations of the evidence to include some previously unknown photographs of the second flag raising, the boards concurred.
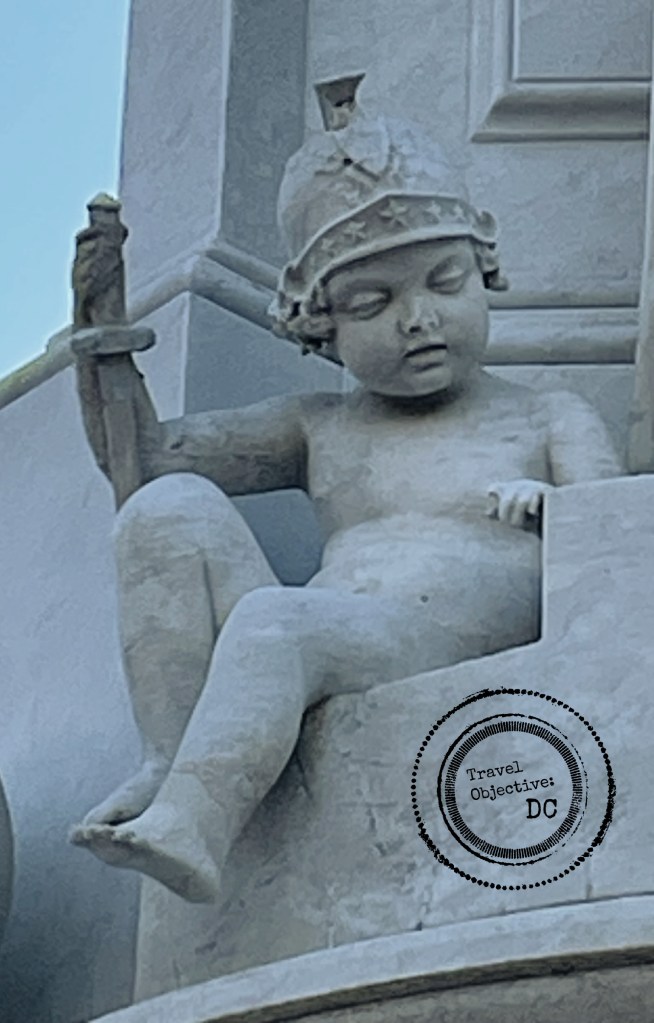
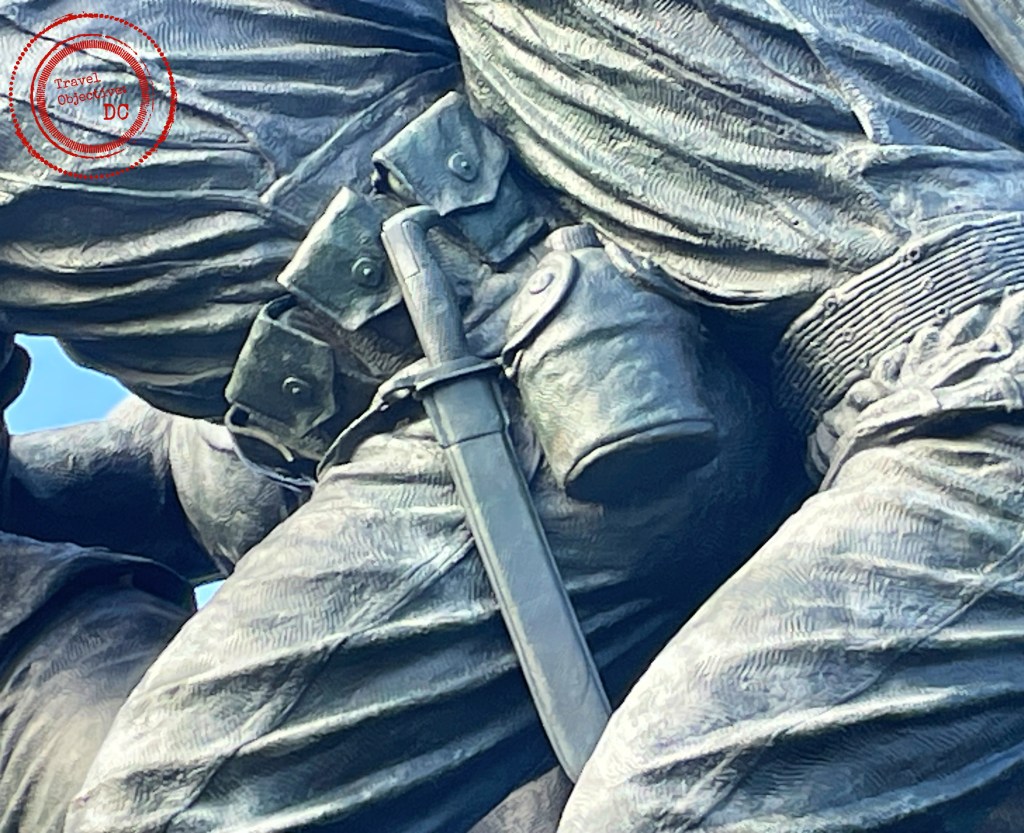
Note the sculptor Felix de Weldon’s precise detail on the Marines’ uniforms and equipment. Given the large size of the statues, the canteen would hold eight gallons of water.

In public statements, the Marines explained the importance of being factually correct, but noted that nothing in the historians’ research nor the boards’ findings diminishes any of the contributions of the Marines and other servicemen who fought on and around Iwo Jima.
Visitors to Washington, DC should include the US Marine Corps War Memorial on their short list of destinations to visit, especially if they have a connection to the Marine Corps. Unlike many other Washington-area landmarks, visiting the Marine Corps Memorial is fairly straightforward. Unless there is a special ceremony, the park is often quiet and peaceful. Free parking is available and the Rosslyn Metro Station is a ten-minute walk away.
But ease in visiting an iconic sculpture is only one reason. Joe Rosenthal’s photograph and the memorial it inspired gained fame for what their subjects represent: critical values, such as teamwork, dedication and sacrifice. These values made the Marine Corps an effective fighting force throughout its history.
Indeed, these values–like the photograph and the monument–are for all time.
* * *

According to the US Marine Corps, the following six Marines are depicted on the memorial (from right to left):
Corporal Harlon Block, (depicted at the base of the flag pole)
Private First Class Harold Keller
Private First Class Franklin Sousley
Sergeant Michael Strand
Private First Class Harold Schultz
Private First Class Ira Hayes
* * *
Route Recon
The US Marine Corps War Memorial is located in Arlington Ridge Park. The address is 1000 Marshall Drive, Arlington, VA 22209.
Park Hours are 6:00 AM – Midnight daily. Restrooms are located at the park.
By Car
From VA 110 south turn right onto Marshall Drive, then follow signs for the US Marine Corps War Memorial.
From US 50 east take the exit for Rosslyn and the Key Bridge. Turn right onto Meade Street at the top of the ramp. Turn left on Marshall Drive, then follow the signs for the US Marine Corps War Memorial.
From US 50 west cross into Virginia on the Roosevelt Bridge and take the exit for Rosslyn and the Key Bridge. Turn left onto Meade Street at the top of the ramp. Turn left on Marshall Drive, then follow the signs for the US Marine Corps War Memorial.
Parking is available at the US Marine Corps War Memorial. Special events may limit parking.
By Metro
The memorial is a 10-15 minute walk from the Rosslyn Metro Station on the Blue Line.
Arlington National Cemetery
Arlington Ridge Park adjoins Arlington National Cemetery. Use Arlington National Cemetery’s Ord & Weitzel Gate gate to access the park and the memorial.
Sunset Parades
On designated Tuesday evenings during the summer, the US Marine Corps holds Sunset Parades at the memorial. The Sunset Parades are a 45-minute performance featuring the US Marine Band, the United States Marine Drum and Bugle Corps and the Marine Corps Silent Drill Platoon.
Command Reading
Flag of Our Fathers – This book was authored by James Bradley, son of Navy Corpsman Jack Bradley who was believed to be one of the flag raisers in Joe Rosenthal’s famous picture. The younger Bradley set out to write a book telling the life stories of the individuals associated with the flag raising. Published in 2000, long before it was concluded that two of the book’s subjects did not actually take part in the flag raising, the book provides compelling background on the lives of these Marines and gripping accounts of the combat on Iwo Jima. Bradley also provides details on how Joe Rosenthal took the famous photo as well the 7th War Loan fundraising campaign.